Concept to Production in Weeks
The journey from concept to production involves several key steps, and each stage is crucial to the success of a product. Here's a general guide outlining the main phases in the process:
Product Categories




- Backpacks
- Crossbody
- Travel Bags
Man Bag
- Shoulder Bag
- Tote Bag
- Mini Bag
- Fabric Bag
Woman Bag

Conceptualization
- Idea Generation: Generate ideas based on market needs, trends, or personal inspiration.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to validate the concept and identify potential competitors.
Design and Planning
- Product Design: Develop detailed design concepts, including sketches, digital renderings, or prototypes.
- Technical Specifications: Create technical specifications that outline materials, dimensions, features, and manufacturing requirements.
- Prototyping: Build prototypes to test and refine the design, ensuring functionality and feasibility.


Feasibility Analysis
- Cost Analysis: Evaluate the cost of production, including materials, labor, and overhead.
- Technical Feasibility: Assess whether the proposed design can be manufactured within technical constraints.
- Market Feasibility: Reassess market conditions and potential demand based on prototypes and initial feedback.
Prototyping and Testing
- Prototype Refinement: Make necessary adjustments based on testing and feedback.
- User Testing: Gather user feedback to ensure the product meets expectations and resolves any issues.
- Quality Assurance: Implement quality control measures to meet industry standards.
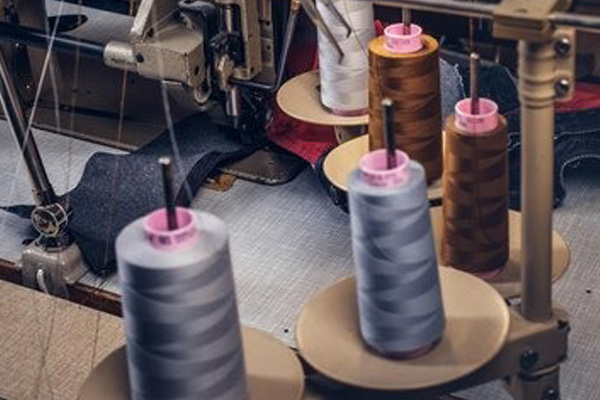


Manufacturing Setup
- Supplier Selection: Identify and establish relationships with reliable suppliers for materials and components.
- Production Facilities: Set up or coordinate with manufacturing facilities to produce the product.
- Production Planning: Develop a production plan, including timelines, quantity projections, and quality control measures.
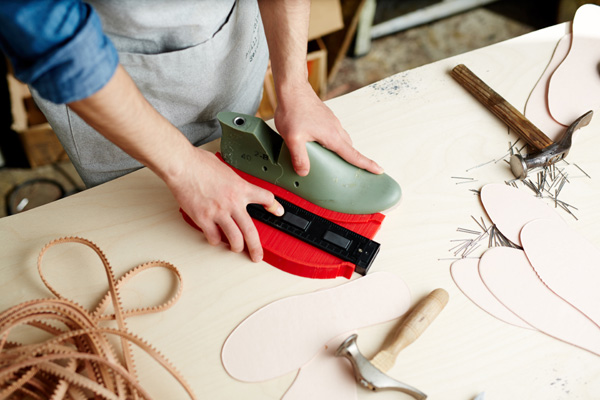
Production
- Material Procurement: Source and purchase required materials and components.
- Assembly: Begin the manufacturing process, assembling the product according to the approved design and specifications.
- Quality Control: Implement quality checks at various stages of production to ensure consistency and compliance.
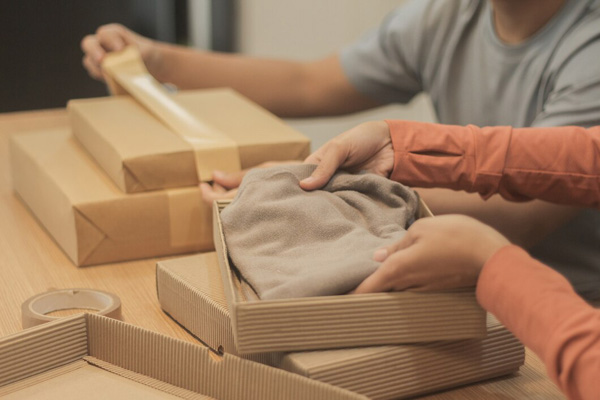


Packaging and Branding
- Packaging Design: Create attractive and functional packaging that aligns with the brand.
- Branding Elements: Incorporate branding elements into the product packaging and labeling.
Distribution and Logistics
- Distribution Channels: Establish distribution channels, considering retail, e-commerce, or other sales platforms.
- Logistics: Plan for the transportation and storage of finished products to reach the market efficiently
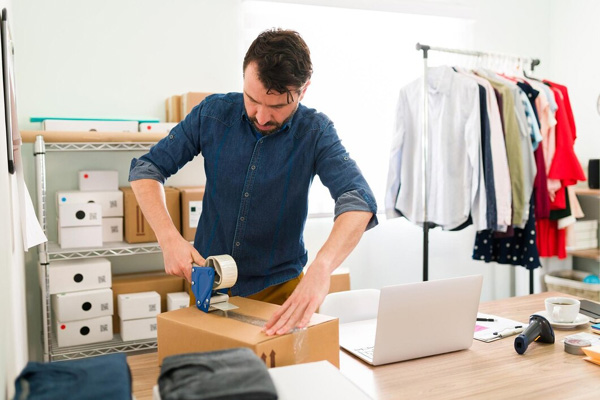


Marketing and Launch
- Marketing Strategy: Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy, including online and offline promotion.
- Launch Campaign: Execute a launch campaign to generate awareness and interest in the product.
Post-Launch Evaluation
- Sales Analysis: Monitor sales performance and gather customer feedback.
- Iterative Improvements: Use post-launch data to make iterative improvements to the product or its marketing strategy.

Scaling
- Scaling Production: If the product is successful, consider scaling production to meet increased demand.
We explore opportunities for product variations or complementary products to expand the product line.
Throughout this process, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability are essential. Each phase should inform the next, and feedback loops should be established to continuously improve the product and its manufacturing processes.